The concept of proxy
Basically in computer networks a proxy server is a server that acts as an intermediary for requests from clients seeking resources from the main servers. The client connects to the proxy server, requesting for a service etc.
Proxies were invented to add structure and encapsulation to distributed systems.
The below block diagram shows the working of proxy
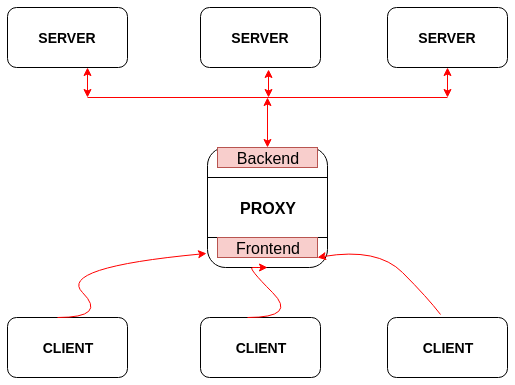
code for having a proxy
1 Defining the context
// defining the context first
void *context = zmq_ctx_new ();
2 Creating the frontend
void *frontend = zmq_socket (context, ZMQ_XSUB);
3 Assigning the static IP
The reason we use static IP and proxies are because they give us the freedom to add more servers / workers without the change in topology.
Let us use IP address localhost:5000 for our frontend.
zmq_connect (frontend, "tcp://localhost:5000");
and use the IP localhost:6000 for our backend where the workers / servers sit.
void *backend = zmq_socket (context, ZMQ_XPUB);
zmq_bind (backend, "tcp://localhost:6000");
4 Run the proxy until the user interrupts
We could poll the frontend and backend sockets and process the request from the clinet and service their requests via server / workers.
But, with the help of zmq_proxy function we can code it in one line.
zmq_proxy (frontend, backend, NULL);