Using Apache Spark - an example
Spark is a general-purpose distributed data processing engine that is suitable for use in a wide range of circumstances. On top of the Spark core data processing engine, there are libraries for SQL, machine learning, graph computation, and stream processing, which can be used together in an application.
The below figure shows the core architecture that spark provides us.

1 - Creating a maven project
We will be coding with java and use maven as our build tool. The below code file shows the maven dependency file pom.xml. Just copy and paste the contents of the file into your pom.xml file that is generated.
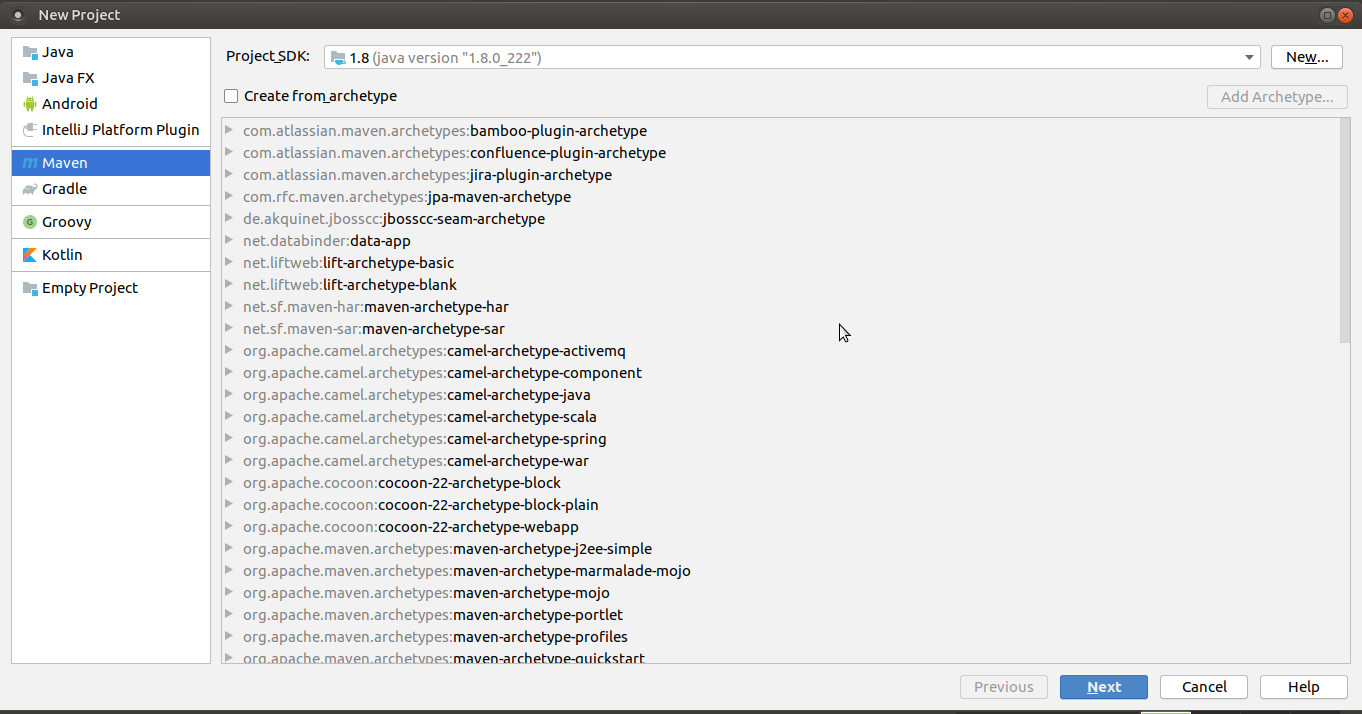
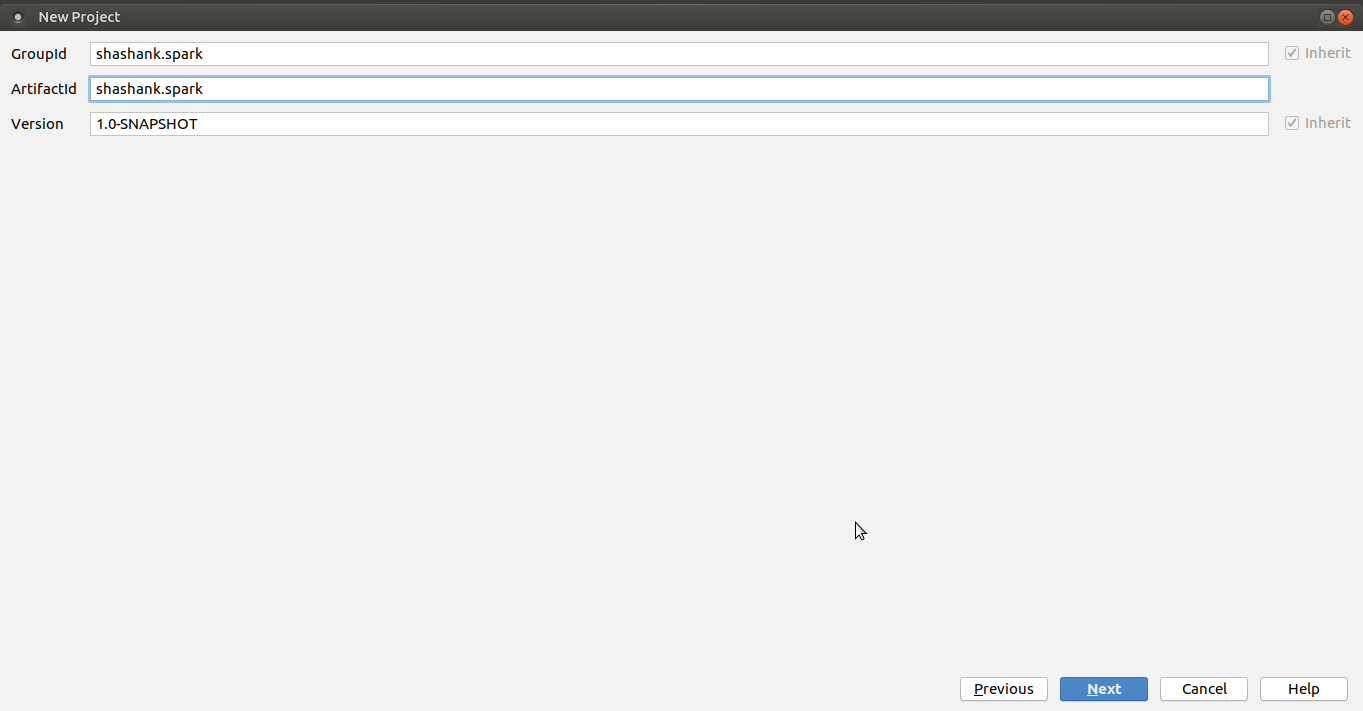
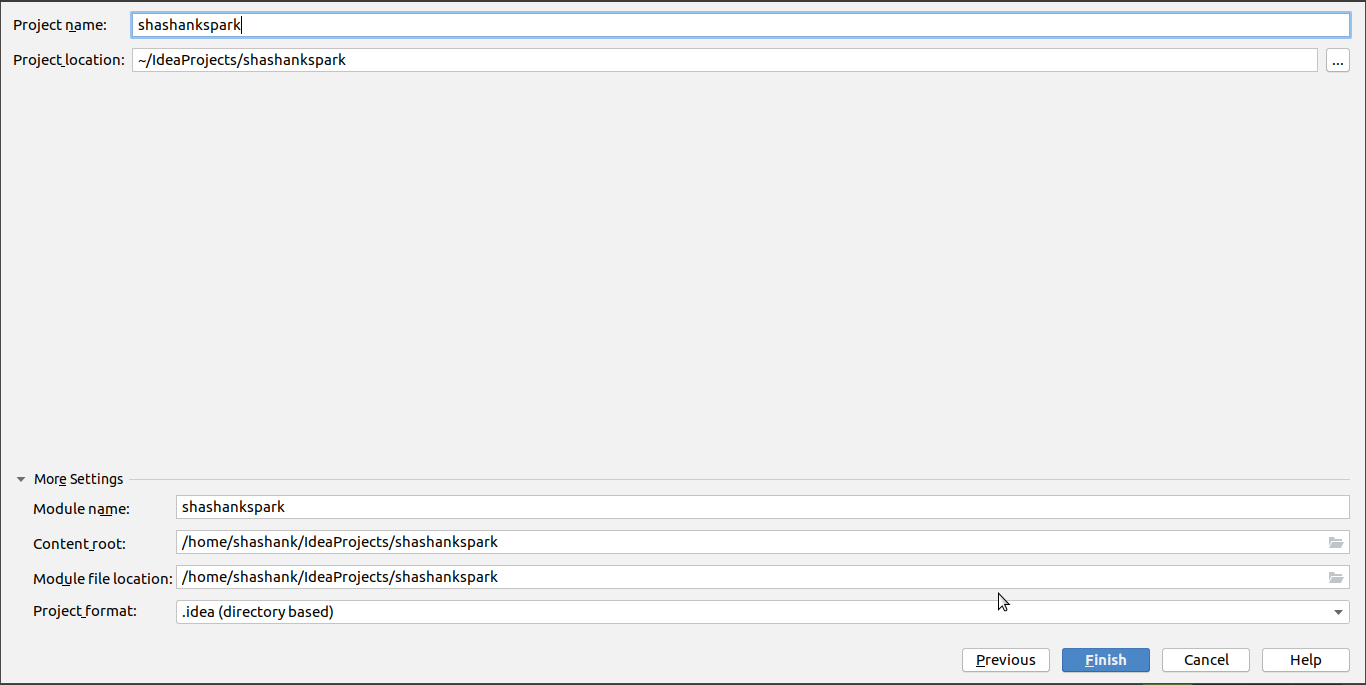
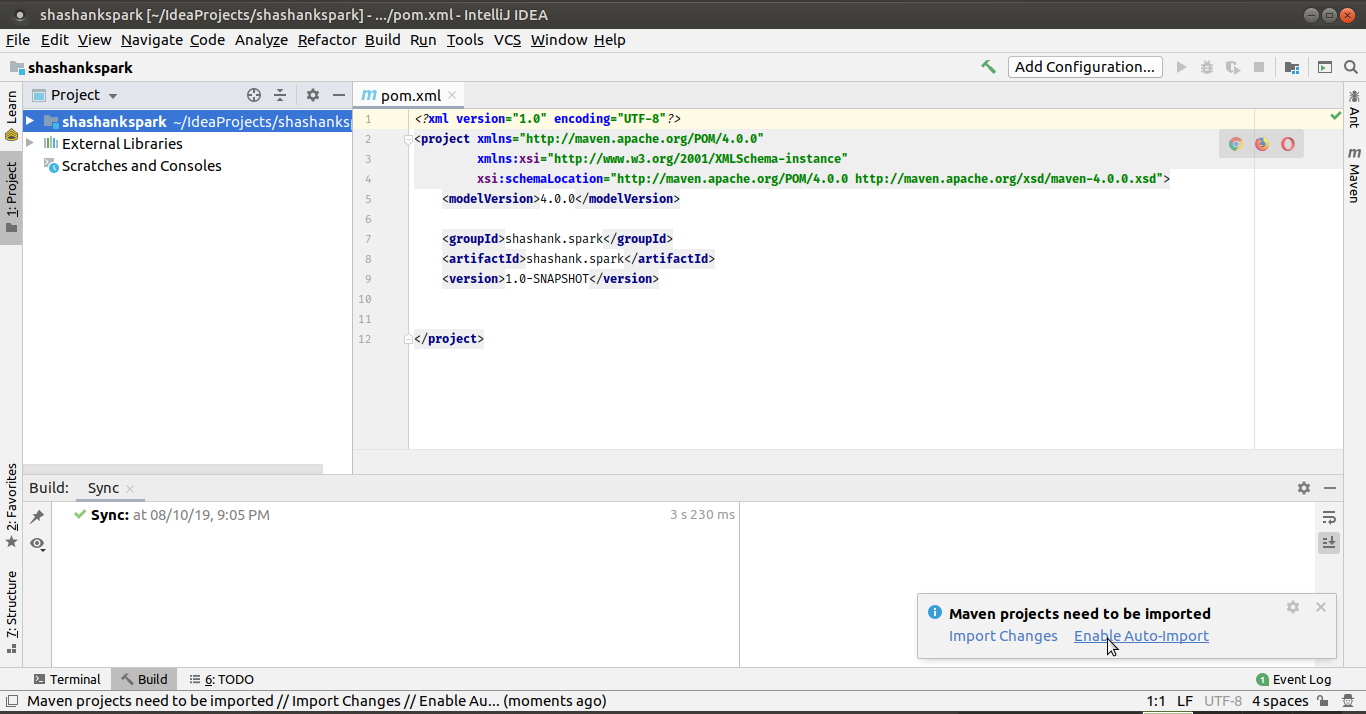
Before that let’s create a barebone maven project. I prefer using Intellij IDEA Community Edition on my Ubuntu Mate Desktop. The below series of pictures shows creating a successful maven project.
Fig : Creating a maven project - step1
Fig: Creating a maven project - step2
Fig: Creating a maven project - step3
Fig: Enable auto import to avoid manual imports everytime
After successful creation of project copy the below dependencies to your pom.xml file. The file can be found here
Maven might take some time depending on your internet connection to download the required dependencies for running spark.
Our basic structure of project might look like the one showed below.
.
├── pom.xml
├── src
│ ├── main
│ │ ├── java
│ │ └── resources
│ └── test
└── target
We now create a main class named Application.java under java directory.
This will be the starting point of our application.
.
├── pom.xml
├── src
│ ├── main
│ │ ├── java
│ │ │ └── Application.java
│ │ └── resources
│ └── test
└── target
Application.java
Let us first import the necessary packages.
import org.apache.spark.sql.Dataset;
import org.apache.spark.sql.Row;
import org.apache.spark.sql.SparkSession;
import static org.apache.spark.sql.functions.*;
The main method
public class Application {
public static void main (String[] args) {
// first let's build a spark session
SparkSession
spark = new
SparkSession.Builder()
.master ("local")
.getOrCreate();
// For dataset - durham-parks.json
// Link - https://catalog.data.gov/dataset/city-parks
Dataset<Row> dfbuildDD = buildDD(spark);
dfbuildDD.show(10);
// For dataset - Philadelphia_recreations.csv
// Link - https://www.opendataphilly.org/dataset
Dataset<Row> dfbuildPPD = buildPPD(spark);
dfbuildPPD.show(20);
}
}
The buildDD method (Processing the durham-parks.json data)
In this method we will read the contents of durham-parks.json file and try to modify some of the rows. We will try to concat new rows to the existing Dataset.
// first we read the Dataset
Dataset<Row>
df = spark
.read()
.format("json")
.option("multiline", true)
.load("src/main/resources/durham-parks.json");
Now we modify the columns. This can we achieved by the function withColumn which is applied on Dataset instance.
df = df.withColumn("park_id",
concat(
df.col("datasetid"),
lit("_"),
df.col("fields.objectid"),
lit("_Durham")
)
)
Similarly, for another column for park_name.
.withColumn(
"park_name",
df.col("fields.park_name")
)
Similarly, for another column for city.
.withColumn(
"city",
lit("Durhma")
)
Similarly, for some other columns.
.withColumn(
"has_playground",
df.col("fields.playground")
)
.withColumn(
"zipcode",
df.col("fields.zip")
)
.withColumn(
"land_in_acres",
df.col("fields.acres")
)
.withColumn(
"geoX",
df.col("geometry.coordinates")
.getItem(0)
)
.withColumn(
"geoY",
df.col("geometry.coordinates")
.getItem(1)
);
At the end we return the Dataset instance df.
return df;
The buildPPD method (Processing the hiladelphia_recreations.csv data)
public static Dataset<Row> buildPPD (SparkSession spark) {
// populate the dataframe
Dataset<Row>
df = spark
.read()
.format("csv")
.option("multiline", true)
.option("header", true)
.load("src/main/resources/philadelphia_recreations.csv");
df = df.filter(
lower(df.col("USE_"))
like("%park%")
);
return df;
}
So when we sun the spark program we get the output which is quite pretty big. You can find the output here.